Problem:
Factorize $ 6x^2 - 7y^2 $
Solution:
$ (\sqrt{6}x + \sqrt{7}y)(\sqrt{6}x - \sqrt{7}y) $
Friday, October 30, 2015
Thursday, October 29, 2015
Interval Notation (3)
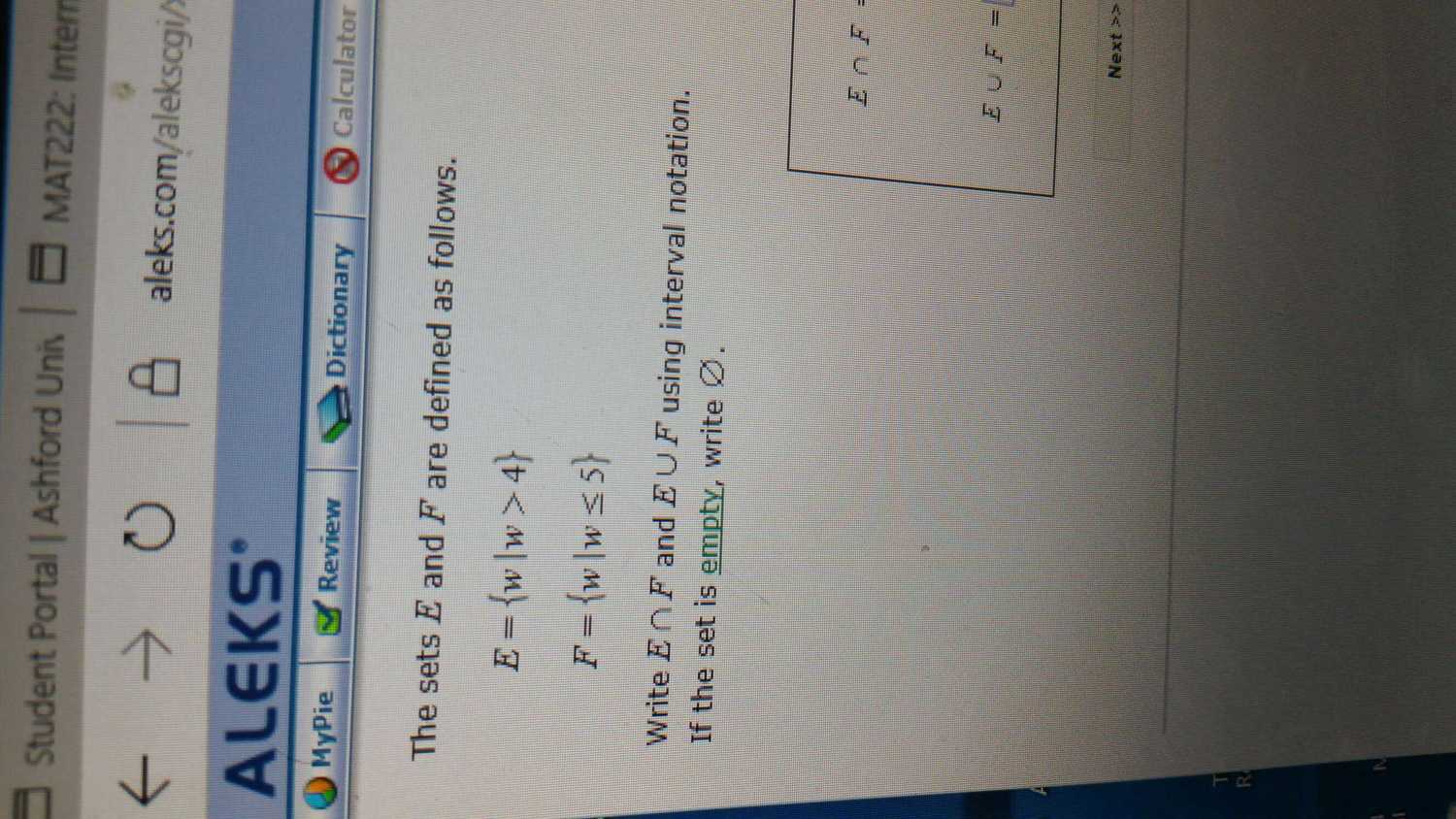
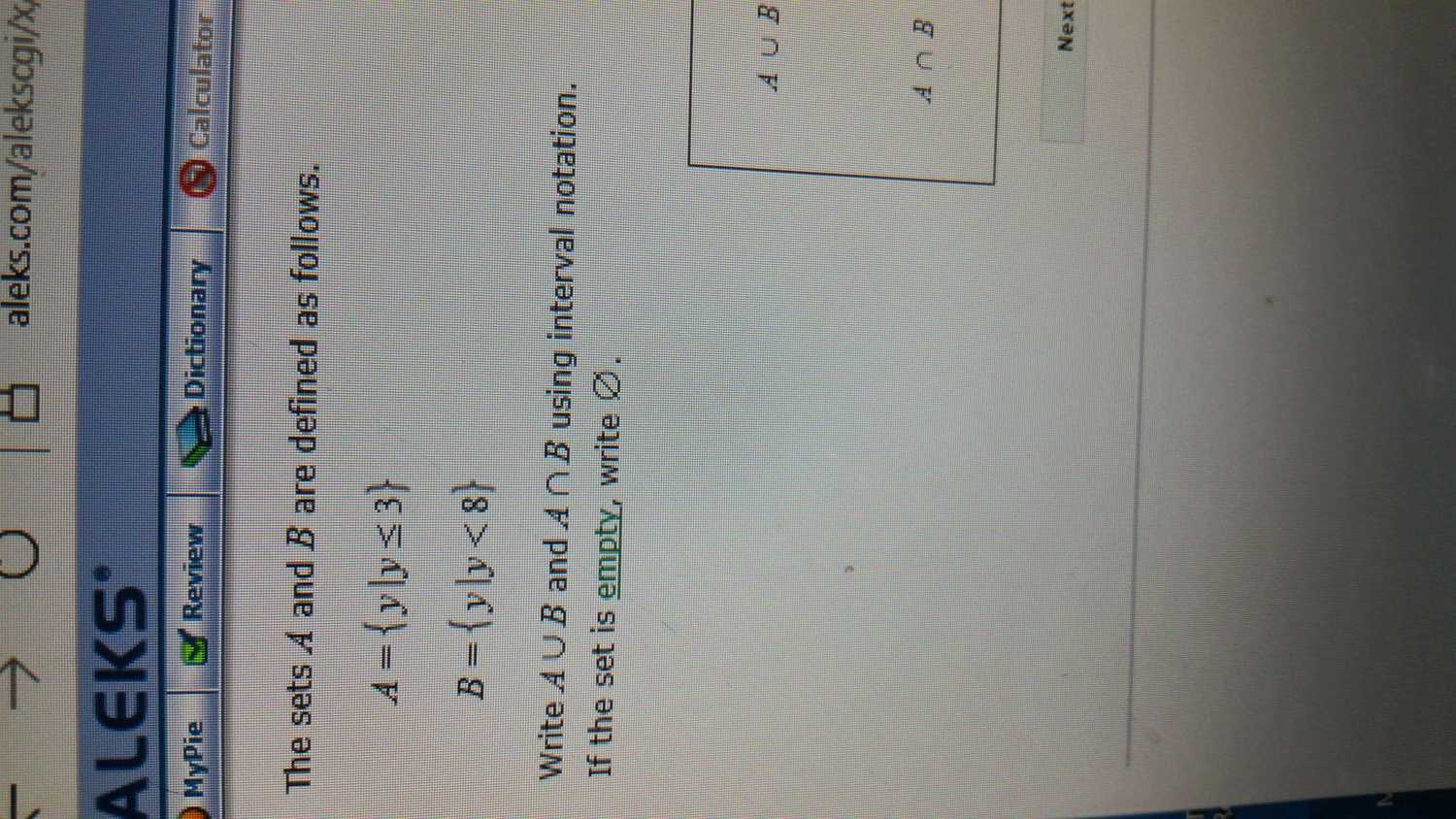
Problem:

Solution:
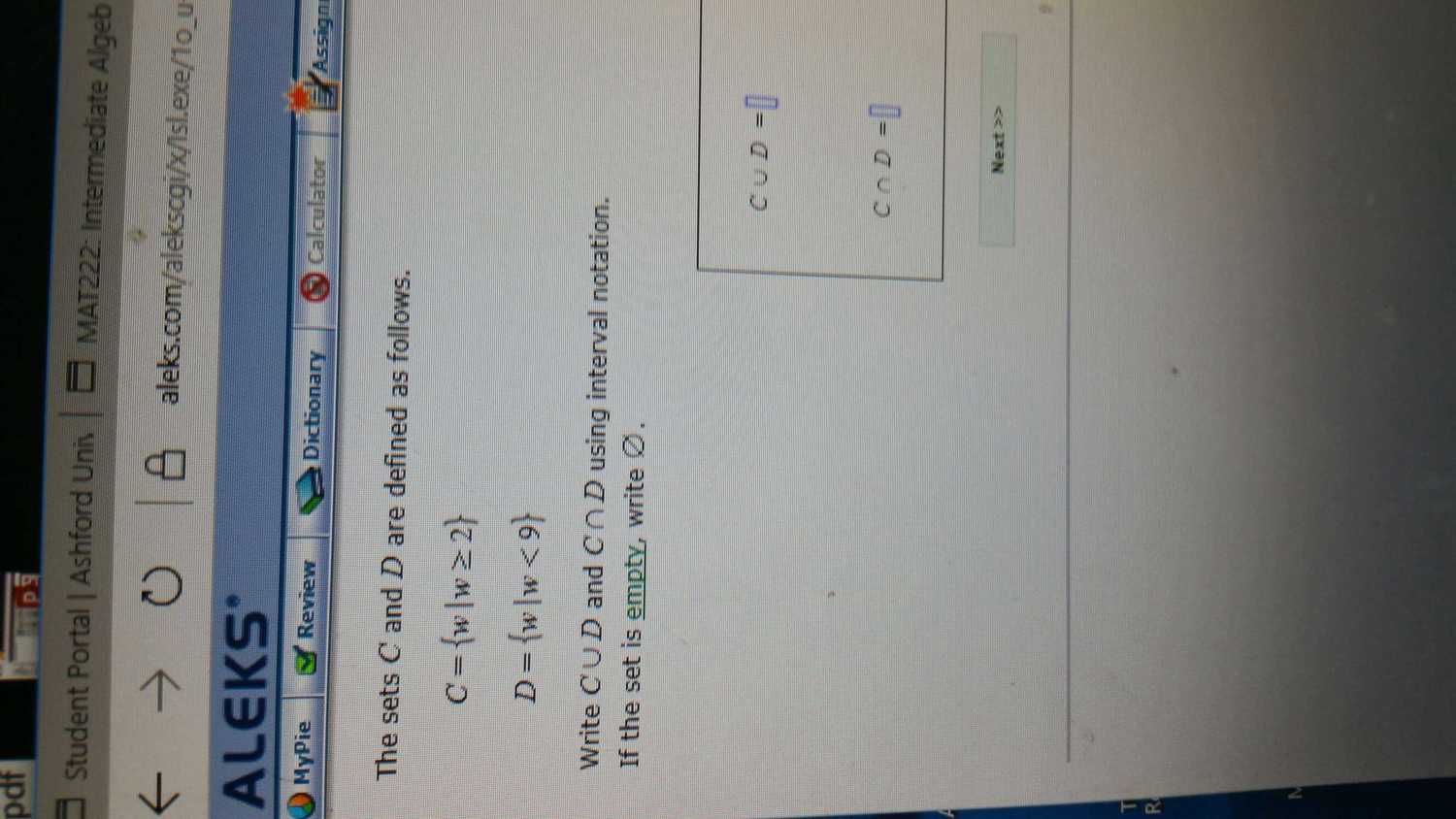
$ A \cup B = (-\infty, 1] \cup (6, \infty) $
$ A \cap B = \emptyset $

Solution:
$ A \cup B = (-\infty, 1] \cup (6, \infty) $
$ A \cap B = \emptyset $
Logarithm
Problem:

Solution:
$ \begin{eqnarray*} & & 6\log(25-x^2)-(\log(5+x)+\log(5-x)) \\ &=& 6\log(25-x^2)-(\log(5+x)(5-x)) \\ &=& 6\log(25-x^2)-\log(25-x^2) \\ &=& 5\log(25-x^2) \\ &=& \log(25-x^2)^5 \\ \end{eqnarray*} $
Angles
Problem:
Solution:
1) 180
2) PQS
3) 130
4) 30
5) 35
6) 100
7) 50
8) 130
9) x = 11, m<DEF = 29, m<FEG = 61
10) x = 10, m <DEF = 91, m<FEG = 89
11) 2, 4
12) 2, 3
13) Right
14) m<KLM = m<KLN = 45
Solution:
1) 180
2) PQS
3) 130
4) 30
5) 35
6) 100
7) 50
8) 130
9) x = 11, m<DEF = 29, m<FEG = 61
10) x = 10, m <DEF = 91, m<FEG = 89
11) 2, 4
12) 2, 3
13) Right
14) m<KLM = m<KLN = 45
Wednesday, October 28, 2015
Matrix
Problem:
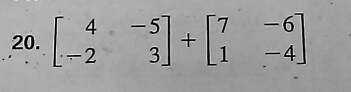
Solution:
$ \left(\begin{array}{cc} 4 & -5 \\ -2 & 3\end{array}\right) + \left(\begin{array}{cc} 7 & -6 \\ 1 & -4\end{array}\right) = \left(\begin{array}{cc} 11 & -11 \\ -1 & -1\end{array}\right) $
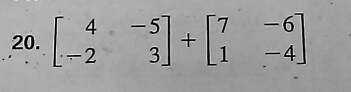
Solution:
$ \left(\begin{array}{cc} 4 & -5 \\ -2 & 3\end{array}\right) + \left(\begin{array}{cc} 7 & -6 \\ 1 & -4\end{array}\right) = \left(\begin{array}{cc} 11 & -11 \\ -1 & -1\end{array}\right) $
Tuesday, October 27, 2015
Summation
Problem:
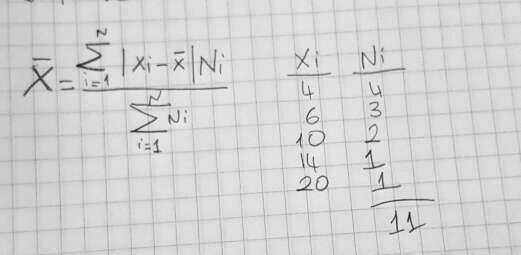
Solution:
$ \bar{x} = 10.8 $.
Here are the values of absolute difference from the mean
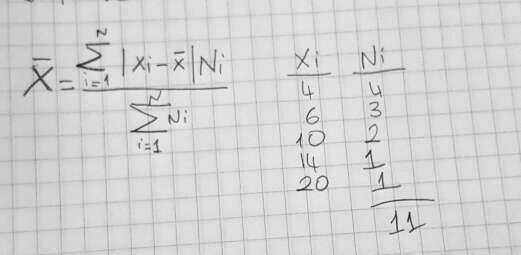
Solution:
$ \bar{x} = 10.8 $.
Here are the values of absolute difference from the mean
| 6.8 |
| 4.8 |
| 0.8 |
| 3.2 |
| 9.2 |
Here are the weighted absolute difference from the mean
| 27.2 |
| 14.4 |
| 1.6 |
| 3.2 |
| 9.2 |
The sum of these numbers is 55.6
Therefore the final result is 5.05454545...
Monday, October 26, 2015
Extra credits
Problem:
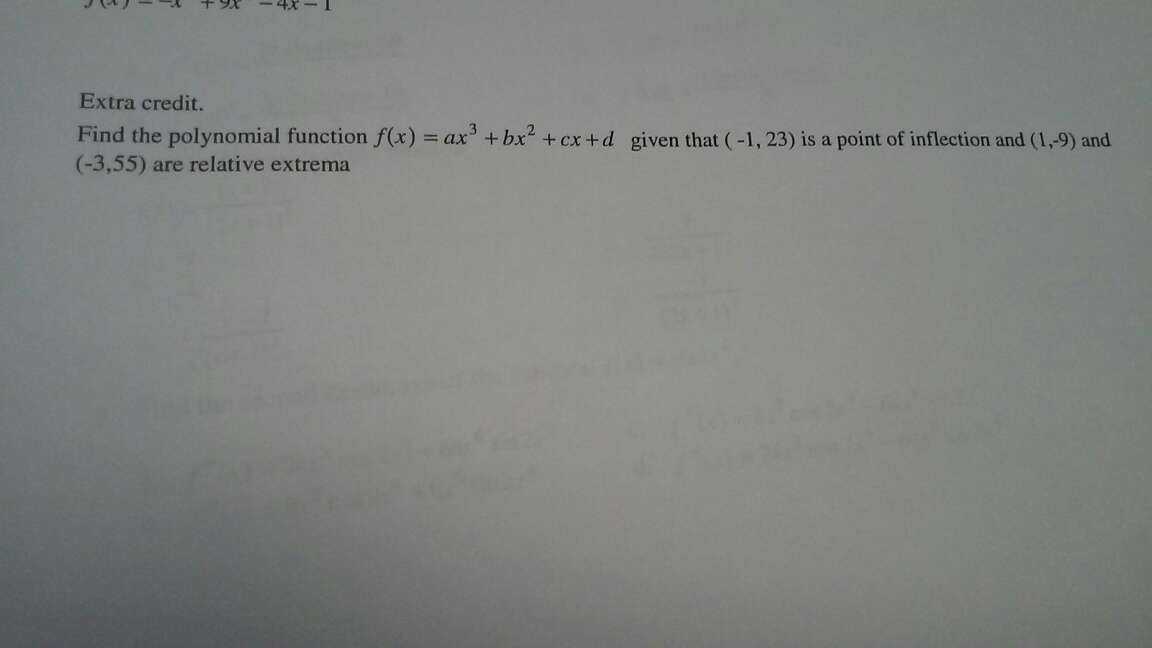
Solution:
$ f'(x) = 3ax^2 + 2bx + c $
$ f''(x) = 6ax + 2b $
The point of inflection has x coordinate -1, therefore
$ 6a(-1) + 2b = 0 $
The extremas has x coordinate 1 and -3, therefore, 1 and -3 are the roots of $3ax^2 + 2bx + c = 0 $
$ 3a + 2b + c = 0 $
$ 3a(-3)^2 + 2b(-3) + c = 0 $.
The three equations tell us $ b = 3a, c = -9a $.
So the equation is $ f(x) = ax^3 + 3ax^2 - 9ax + d$
When x = 1, $ f(x) = a + 3a - 9a + d = -5a + d = -9 $
When x = -1, $ f(x) = -a + 3a + 9a + d = 11a + d = 23 $
Therefore $ a = 2, d = 1 $
The final answer is $ 2x^3 + 6x^2 - 18x + 1 $
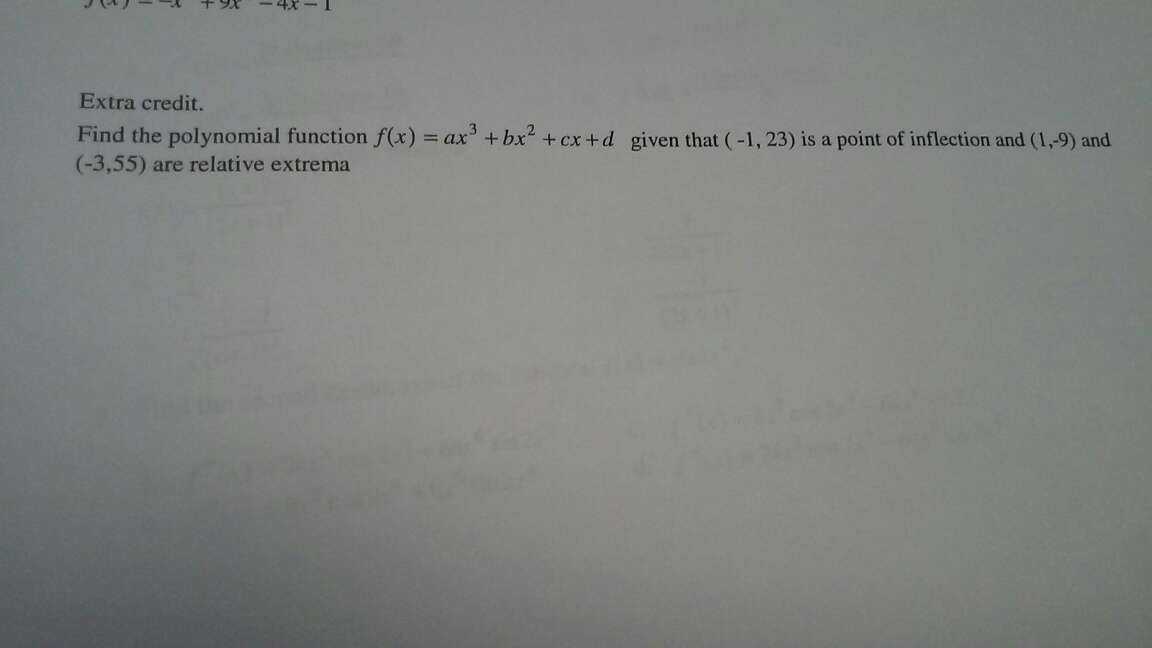
Solution:
$ f'(x) = 3ax^2 + 2bx + c $
$ f''(x) = 6ax + 2b $
The point of inflection has x coordinate -1, therefore
$ 6a(-1) + 2b = 0 $
The extremas has x coordinate 1 and -3, therefore, 1 and -3 are the roots of $3ax^2 + 2bx + c = 0 $
$ 3a + 2b + c = 0 $
$ 3a(-3)^2 + 2b(-3) + c = 0 $.
The three equations tell us $ b = 3a, c = -9a $.
So the equation is $ f(x) = ax^3 + 3ax^2 - 9ax + d$
When x = 1, $ f(x) = a + 3a - 9a + d = -5a + d = -9 $
When x = -1, $ f(x) = -a + 3a + 9a + d = 11a + d = 23 $
Therefore $ a = 2, d = 1 $
The final answer is $ 2x^3 + 6x^2 - 18x + 1 $
Point of inflection
Problem:

Solution:
The point of inflection is where the second derivative is 0, so we compute the second derivative as follow:
$ f'(x) = -3x^2 + 18x - 4 $
$ f''(x) = -6x + 18 $
Therefore the point of inflection has x coordinate 3, the y coordinate is $ -(3)^3 + 9 \times 3^2 - 4 \times 3 - 1 = 119 $
The curve is concave up in $ (-\infty, 3) $ and is concave down in $ (3, \infty) $.

Solution:
The point of inflection is where the second derivative is 0, so we compute the second derivative as follow:
$ f'(x) = -3x^2 + 18x - 4 $
$ f''(x) = -6x + 18 $
Therefore the point of inflection has x coordinate 3, the y coordinate is $ -(3)^3 + 9 \times 3^2 - 4 \times 3 - 1 = 119 $
The curve is concave up in $ (-\infty, 3) $ and is concave down in $ (3, \infty) $.
Sunday, October 25, 2015
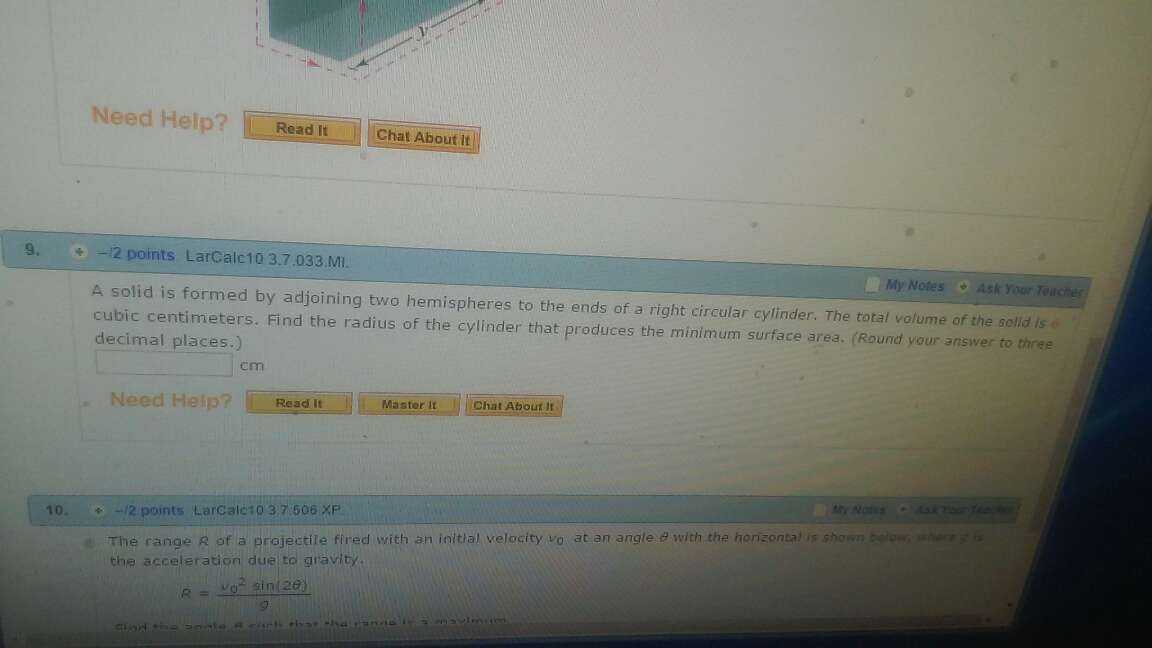
Solid
Problem:
Solution:
Minimize $ 4\pi r^2 + 2\pi r h $ subject to $ \frac{4}{3}\pi r^3 + \pi r^2 h = 6 $.
The Lagrangian is $ 4\pi r^2 + 2\pi r h - \lambda(\frac{4}{3}\pi r^3 + \pi r^2 h - 6) $.
The partial derivatives must be 0, so we have
$ 8\pi r + 2\pi h - \lambda (4 \pi r^2 + 2\pi r h) = 0 $
$ 2 \pi r - \lambda(\pi r^2) = 0 $
The second equation implies $ \lambda = \frac{2}{r} $.
Substitute this back to the first equation, solving get $ h = 0 $.
This seems reasonable because we know sphere maximize volume and minimize surface area, it only make sense if the cylindrical part vanish.
So it is simple now, $ \frac{4}{3}\pi r^3 = 6 $, $ r = \sqrt[3]{\frac{9}{2\pi}} = 1.127251652 $.

Solution:
Minimize $ 4\pi r^2 + 2\pi r h $ subject to $ \frac{4}{3}\pi r^3 + \pi r^2 h = 6 $.
The Lagrangian is $ 4\pi r^2 + 2\pi r h - \lambda(\frac{4}{3}\pi r^3 + \pi r^2 h - 6) $.
The partial derivatives must be 0, so we have
$ 8\pi r + 2\pi h - \lambda (4 \pi r^2 + 2\pi r h) = 0 $
$ 2 \pi r - \lambda(\pi r^2) = 0 $
The second equation implies $ \lambda = \frac{2}{r} $.
Substitute this back to the first equation, solving get $ h = 0 $.
This seems reasonable because we know sphere maximize volume and minimize surface area, it only make sense if the cylindrical part vanish.
So it is simple now, $ \frac{4}{3}\pi r^3 = 6 $, $ r = \sqrt[3]{\frac{9}{2\pi}} = 1.127251652 $.
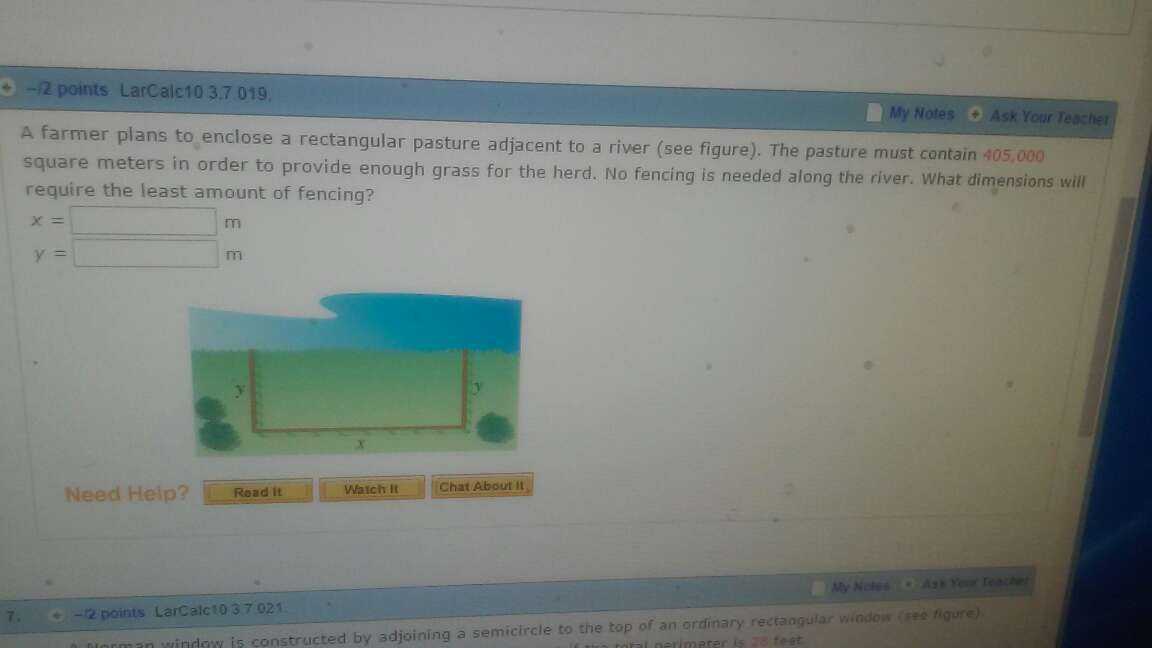
Farmer knew Lagrangian optimization!
Problem:
Solution:
Minimize x + 2y subject to xy = 405000
The Lagrangian is
$ L(x, y, \lambda) = x + 2y + \lambda(xy - 405000) $
The partial derivatives must be 0, so we get
$ 1 + \lambda y = 0 $
$ 2 + \lambda x = 0 $
Multiply the first equation by $ x $ and multiply the second equation by $ y $ gives $ x - 2y = 0 $.
In other words, $ x = 2y $, so $ xy = 2y^2 = 405000 $, $ y = 450, x = 900 $.

Solution:
Minimize x + 2y subject to xy = 405000
The Lagrangian is
$ L(x, y, \lambda) = x + 2y + \lambda(xy - 405000) $
The partial derivatives must be 0, so we get
$ 1 + \lambda y = 0 $
$ 2 + \lambda x = 0 $
Multiply the first equation by $ x $ and multiply the second equation by $ y $ gives $ x - 2y = 0 $.
In other words, $ x = 2y $, so $ xy = 2y^2 = 405000 $, $ y = 450, x = 900 $.
Friday, October 23, 2015
Limit
Problem:
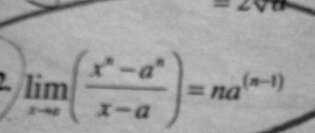
Solution:
$ \frac{x^n - a^n}{x-a} = \frac{(x - a)(x^{n - 1} + ax^{n-2} + .. + a^{n-1})}{x - a} = (x^{n - 1} + ax^{n-2} + .. + a^{n-1}) $
Therefore $ \lim\limits_{x \to a}\frac{x^n - a^n}{x-a} = \lim\limits_{x \to a} (x^{n - 1} + ax^{n-2} + .. + a^{n-1}) = na^{n-1} $.
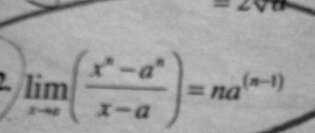
Solution:
$ \frac{x^n - a^n}{x-a} = \frac{(x - a)(x^{n - 1} + ax^{n-2} + .. + a^{n-1})}{x - a} = (x^{n - 1} + ax^{n-2} + .. + a^{n-1}) $
Therefore $ \lim\limits_{x \to a}\frac{x^n - a^n}{x-a} = \lim\limits_{x \to a} (x^{n - 1} + ax^{n-2} + .. + a^{n-1}) = na^{n-1} $.
Thursday, October 22, 2015
Population
Problem:

Solution:
a) $ f(t) = 30 \times e^0.017t $
b) 41.43796053
c) 1.017145322
d) times
Solution:
a) $ f(t) = 30 \times e^0.017t $
b) 41.43796053
c) 1.017145322
d) times
Finance 5
Problem:

Solution:
a)
Solution:
a)
Times
|
APY (Decimal)
|
APY (Percentage)
|
1
|
0.052
|
5.2%
|
12
|
0.053257411
|
5.325741057%
|
365
|
0.053371841
|
5.337184107%
|
Continuously
|
0.053375743
|
5.337574251%
|
b) 26912.4424
Finance 4
Problem:

Solution:
a) 2347.021742
b) $ f(t) = 2000 \times e^{\frac{3.2}{100}} $
c) $ e^{\frac{3.2}{100}} - 1 = 0.032517505 = 3.251750531\%$
d) $ (e^{\frac{3.2}{100}})^{10} - 1 = 0.377127764 = 37.71277643 \%$
Solution:
a) 2347.021742
b) $ f(t) = 2000 \times e^{\frac{3.2}{100}} $
c) $ e^{\frac{3.2}{100}} - 1 = 0.032517505 = 3.251750531\%$
d) $ (e^{\frac{3.2}{100}})^{10} - 1 = 0.377127764 = 37.71277643 \%$
Finance 2
Problem:

Solution:
To be continued with part b when the choices are available.
Solution:
|
Year
|
Monthly
|
Daily
|
Continuously
|
|
1
|
4825.305364
|
4826.254424
|
4826.286816
|
|
2
|
5174.127079
|
5176.162615
|
5176.232095
|
|
4
|
5949.24245
|
5953.924315
|
5954.084156
|
|
10
|
9043.476195
|
9061.279018
|
9061.887184
|
|
30
|
36524.23864
|
36740.36641
|
36747.76461
|
|
APY
|
7.229008086%
|
7.250098317%
|
7.250818125%
|
To be continued with part b when the choices are available.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)